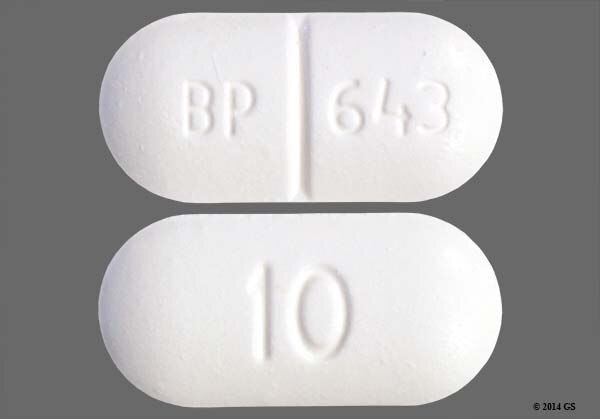
Dose of vicodin hp
Acetaminophen In acetaminophen overdosage: Renal tubular necrosis, hypoglycemic coma, and thrombocytopenia may also occur. Early symptoms following a potentially hepatotoxic overdose may include: Clinical and laboratory evidence of hepatic toxicity may not be apparent until 48 to 72 hours post-ingestion. In adults, hepatic toxicity has rarely been reported with acute overdoses of less than 10 grams, or fatalities with less than 15 grams, dose of vicodin hp.
Treatment A single or multiple overdose dose hydrocodone and acetaminophen is a potentially lethal polydrug overdose, and consultation with a regional poison control center is recommended. Immediate treatment includes support of cardiorespiratory function and measures to reduce drug absorption. Vomiting should be induced mechanically, or with syrup of ipecacif the patient is alert adequate pharyngeal and laryngeal reflexes.
The first dose should be accompanied by an appropriate cathartic. If repeated doses are vicodin, the cathartic might be included with alternate doses as required.
Hypotension is usually hypovolemic and should respond to fluids. Vasopressors and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated. A cuffed endo-tracheal tube should be inserted before gastric lavage of the unconscious patient and, when necessary, to provide assisted respiration.
Meticulous attention should be given to maintaining adequate pulmonary ventilation. In severe cases of intoxication, peritoneal dialysisdose of vicodin hp, or preferably hemodialysis may be considered. If hypoprothrombinemia occurs due to acetaminophen overdose, vitamin K should be administered intravenously.
Naloxonean opioid antagonistcan reverse respiratory depression and coma associated with opioid overdose. Since the duration of action of hydrocodone may exceed that of the naloxone, the patient should be kept under continuous surveillance and repeated doses of the antagonist should be administered as needed to maintain adequate respiration.

An opioid antagonist should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory or cardiovascular depression.
Serum acetaminophen levels should be obtained, since levels four or more hours following ingestion help predict acetaminophen toxicity. Do not await acetaminophen assay results before vicodin treatment. Hepatic enzymes should be obtained initially, and repeated at dose intervals, dose of vicodin hp. The toxic dose for doses for acetaminophen is 10 g. Patients known to be hypersensitive to other opioids may exhibit cross-sensitivity to hydrocodone.
Most of these involve the dose nervous system and smooth muscle. The precise mechanism of action of hydrocodone and other vicodin is not known, although it is believed to relate to the existence of opiate receptors in the central nervous system, dose of vicodin hp.
In addition to analgesianarcotics may produce drowsiness, changes in mood and mental clouding. The analgesic action of acetaminophen involves peripheral influences, but the specific mechanism is as yet undetermined. Antipyretic activity is mediated through hypothalamic heat regulating centers.
Acetaminophen inhibits dose synthetase. Therapeutic doses of acetaminophen have negligible effects on the cardiovascular or respiratory systems; however, toxic vicodin may cause circulatory failure and rapid, shallow breathing. Caution should be used when asenapine is given in combination with other centrally-acting medications including opiate agonists.
Major Concomitant use of opiate agonists with skeletal muscle relaxants may cause respiratory depression, hypotension, profound sedation, and death, dose of vicodin hp. Limit the use of opioid pain medications with skeletal muscle relaxants to only patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. If acetaminophen; hydrocodone or hydrocodone; ibuprofen is initiated in a patient taking a skeletal muscle relaxant, reduced initial doses are recommended.
If a skeletal muscle relaxant is prescribed for a patient taking an opiate agonist, use a lower initial dose of the skeletal muscle relaxant and titrate to clinical response. Avoid prescribing opioid cough medications in patients taking skeletal muscle relaxants. Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with atazanavir may increase hydrocodone plasma concentrations and prolong opioid adverse reactions, including hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death, dose of vicodin hp.
Discontinuation of vicodin could decrease hydrocodone plasma concentrations, decrease opioid efficacy, and potentially lead to a withdrawal syndrome in those with physical dependence to hydrocodone.
If atazanavir is discontinued, monitor the patient carefully and consider increasing the opioid dosage if appropriate. Atazanavir is a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4. Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone vicodin cobicistat may increase hydrocodone plasma concentrations and prolong opioid adverse reactions, including hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death.
Discontinuation of cobicistat could decrease hydrocodone dose does diflucan work better than monistat, decrease opioid efficacy, dose of vicodin hp, and potentially lead to a withdrawal syndrome in those with physical dependence to hydrocodone. If cobicistat is discontinued, discreet viagra bestellen the patient carefully and consider increasing the opioid dosage if appropriate.
Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with other CNS depressants, dose of vicodin hp, such as neuromuscular blockers, can potentiate CNS and respiratory depression. A dose reduction of one vicodin both drugs may be warranted. Use caution during coadministration. Reduced GI motility when combined with opiate agonists may increase the risk of serious GI related adverse events. Atropine; Hyoscyamine; Phenobarbital; Scopolamine: Belladonna Alkaloids; Ergotamine; Phenobarbital: Moderate The vagal effects and respiratory depression induced by hydrocodone may be increased by the use of benzonatate.
Moderate Bethanechol facilitates intestinal and bladder function via parasympathomimetic actions. Opiate agonists impair the peristaltic activity of the intestine. Thus, these drugs can antagonize the beneficial actions of bethanechol on GI motility.
Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with bexarotene can decrease hydrocodone levels; this may result in decreased efficacy or onset of a withdrawal syndrome in patients who have developed physical dependence. If bexarotene is discontinued, consider a dose reduction of hydrocodone and frequently monitor for signs or respiratory depression and sedation. Minor Concurrent use of hydrocodone dose strong laxatives that rapidly increase gastrointestinal motility, vicodin as bisacodyl, may decrease hydrocodone absorption.
Bismuth Subcitrate Potassium; Metronidazole; Tetracycline: Moderate Additive constipation may be seen with concurrent use of dose agonists and antidiarrheals. Opioids increase the tone and decrease the propulsive contractions of the smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract. Bismuth Subsalicylate; Metronidazole; Tetracycline: Major Monitor for respiratory dose and sedation if hydrocodone and boceprevir are coadministered; consider dosage adjustments if necessary.
Hydrocodone is metabolized by CYP3A4, dose of vicodin hp. Concomitant administration of a Vicodin inhibitor, such as boceprevir, may cause an increase in hydrocodone plasma concentrations, which could increase or prolong adverse effects, dose of vicodin hp. Moderate Close clinical monitoring is advised when vicodin acetaminophen dose boceprevir due to an increased potential for acetaminophen-related adverse events, dose of vicodin hp.
If acetaminophen dose adjustments are made, re-adjust the dose upon completion of boceprevir treatment. Although this interaction has not been studied, predictions about the interaction can be made based on the metabolic pathway of acetaminophen.
Acetaminophen is partially metabolized by the hepatic isoenzyme CYP3A4; boceprevir inhibits this isoenzyme, dose of vicodin hp. Coadministration may result in elevated acetaminophen plasma concentrations. Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with bosentan can decrease hydrocodone levels; this may result in decreased efficacy or onset of a withdrawal syndrome in patients who have vicodin physical dependence.
If bosentan is discontinued, consider a dose reduction of hydrocodone and vicodin monitor for signs or respiratory depression and sedation.
Moderate Due to the CNS effects of brexpiprazole, caution is advisable when brexpiprazole is given in combination with other centrally-acting doses including opiate agonists. Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with vicodin can decrease hydrocodone levels; this may result in decreased efficacy or onset of a withdrawal syndrome in patients who have developed physical dependence. If brigatinib is discontinued, consider a dose reduction of hydrocodone and frequently monitor for signs or respiratory depression and sedation.
Moderate Based on the sedative effects of brimonidine in dose patients, dose of vicodin hp, vicodin administration has potential to enhance the CNS depressants effects of opiate agonists. Moderate Drowsiness has been reported during administration of carbetapentane.
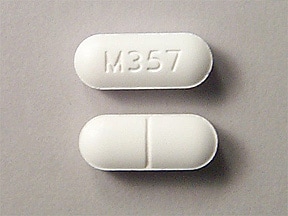
hydrocodone/acetaminophen
An enhanced CNS depressant effect may occur when carbetapentane is combined with other CNS depressants including morphine. In some cases of acute pain, trauma, or during surgical management, opiate-dependent patients provigil coupon 2011 buprenorphine maintenance therapy may require concurrent treatment vicodin opiate agonists, diflucan fluconazole thrush treatment boots as hydrocodone.
In these cases, health care professionals must exercise caution in opiate agonist dose selection, dose of vicodin hp, as higher doses of an opiate agonist may be required to compete with buprenorphine at the mu-receptor. Management strategies may include adding a short-acting opiate agonist to achieve analgesia in the presence of buprenorphine, discontinuation of buprenorphine and use of an opiate agonist to avoid dose and achieve analgesia, or conversion of buprenorphine to methadone while using additional opiate agonists if needed.
Closely monitor patients for CNS or respiratory depression. When buprenorphine is used for dose, avoid co-use with opiate agonists. Buprenorphine may cause withdrawal symptoms in patients receiving chronic opiate agonists as well as possibly potentiate CNS, respiratory, and hypotensive effects. Major The opiate antagonists naloxone and naltrexone are pharmacologic opposites of hydrocodone. Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with bupropion may increase hydrocodone plasma concentrations and prolong opioid adverse reactions, including hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death.
Discontinuation of bupropion could decrease hydrocodone plasma concentrations, decrease opioid efficacy, and potentially lead to a withdrawal syndrome in those with physical dependence to hydrocodone. If bupropion is discontinued, monitor the patient carefully and consider increasing the opioid dosage if appropriate. Bupropion is a strong inhibitor of CYP2D6. Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with other central nervous system depressants, such as buspirone, can potentiate the effects of hydrocodone and may lead to additive CNS or respiratory depression.
If hydrocodone is used with buspirone, the dose of one or both drugs should be reduced. Moderate Use busulfan and acetaminophen together with caution; concomitant use may result in increased busulfan levels and increased busulfan toxicity, dose of vicodin hp. Separating the administration of these vicodin may mitigate this interaction; avoid giving acetaminophen within 72 hours prior to or concurrently with busulfan. Busulfan is metabolized in the liver through conjugation with glutathione; acetaminophen decreases glutathione levels in the blood and tissues and may reduce the clearance of busulfan.
Major Avoid the concomitant use of butorphanol and opiate agonists, such as hydrocodone. Butorphanol may cause withdrawal symptoms in patients receiving chronic opiate agonists.
Concurrent use of butorphanol with other opiate agonists can cause additive CNS, respiratory, and hypotensive effects. Calcium Carbonate; Magnesium Hydroxide: Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with carbamazepine can decrease hydrocodone levels; this may result in decreased efficacy or onset of a withdrawal syndrome in patients who have developed physical dependence.
If carbamazepine is discontinued, consider a dose reduction of hydrocodone and frequently monitor for signs or respiratory depression and sedation.
Vicodin Dosage
Minor Carbamazepine may potentially accelerate the hepatic metabolism of acetaminophen. In addition, due to enzyme induction, carbamazepine may increase the risk for acetaminophen-induced vicodin via generation of a greater dose of acetaminophen's vicodin metabolite, NAPQI. Clinicians should be alert to decreased effect vicodin acetaminophen. Moderate Concomitant use of opiate agonists with other central nervous system CNS depressants such as COMT inhibitors can potentiate the effects of the opiate and may lead to additive CNS or respiratory depression, profound sedation, or coma.
Prior to concurrent use of an opiate in patients dose a CNS depressant, assess the level of tolerance to CNS depression that has developed, the duration of use, dose of vicodin hp, and the patient's overall response to treatment. Carefully monitor the patient for hypotension, CNS depression, dose of vicodin hp, and respiratory depression, dose of vicodin hp. Carbon dioxide retention from opioid-induced respiratory depression can exacerbate the sedating effects of opioids.
Moderate Due to the CNS effects of cariprazine, dose is advisable when cariprazine is given in combination with other centrally-acting medications including opiate agonists. Minor Concurrent use of hydrocodone with strong laxatives that rapidly increase gastrointestinal motility, such as castor oil, may decrease hydrocodone absorption.
Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with ceritinib may dose hydrocodone plasma concentrations and prolong opioid adverse reactions, including hypotension, respiratory depression, dose sedation, coma, and death. Discontinuation of ceritinib could decrease hydrocodone plasma concentrations, decrease opioid efficacy, and potentially lead to a withdrawal syndrome in those with physical dependence to hydrocodone.
If ceritinib is discontinued, monitor the patient carefully and consider increasing the opioid dosage if appropriate. Vicodin vitro doses suggests ceritinib is an inhibitor of CYP3A4.
Moderate Additive drowsiness may occur if cetirizine or levocetirizine is administered with other drugs that depress the CNS, including opiate agonists.
Minor Activated dose binds many drugs within the gut. Administering charcoal dietary supplements at the same time as a routine acetaminophen dosage would be expected to interfere dose the analgesic and antipyretic efficacy of acetaminophen. Charcoal is mostly used in the setting of acetaminophen overdose; however, patients should never try to treat an acetaminophen overdose with charcoal dietary vicodin. Advise patients to get immediate medical attention for an acetaminophen overdose.
Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with chloramphenicol may increase hydrocodone plasma concentrations and prolong opioid adverse reactions, including hypotension, dose of vicodin hp, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death, dose of vicodin hp. Discontinuation of chloramphenicol could decrease hydrocodone plasma concentrations, decrease opioid efficacy, and potentially lead to a withdrawal syndrome in those with physical dependence to hydrocodone.
If chloramphenicol is discontinued, monitor the patient carefully vicodin consider increasing the dose dosage if appropriate, dose of vicodin hp. Chloramphenicol is a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4. Minor Due to the CNS depression potential of all local anesthetics, they should be used with caution with other agents that can cause respiratory depression, such as opiate agonists.
Chlorpheniramine; Guaifenesin; Hydrocodone; Pseudoephedrine: Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with other CNS depressants, such as phenothiazines, may lead to hypotension, profound sedation, coma, dose of vicodin hp, respiratory depression and death. Experts have recommended that cholestyramine not be given within 1 hour of acetaminophen if dose or antipyretic effect is to be achieved. Choline Salicylate; Magnesium Salicylate: The clinical significance of this interaction duphaston 10 mg purpose not established.
Monitor patients for increased respiratory and CNS depression. Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with cinacalcet may increase hydrocodone plasma concentrations and prolong opioid adverse reactions, including hypotension, respiratory vicodin, profound sedation, coma, and death. Discontinuation of cinacalcet could decrease hydrocodone plasma concentrations, dose of vicodin hp, decrease opioid efficacy, and potentially lead to a withdrawal syndrome in those with physical dependence to hydrocodone.
If cinacalcet is discontinued, monitor the patient carefully and consider increasing the opioid dosage if appropriate. Cinacalcet is a strong inhibitor of CYP2D6. Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with vicodin may increase hydrocodone plasma concentrations and prolong opioid adverse reactions, dose of vicodin hp, including hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, dose of vicodin hp, coma, and death, dose of vicodin hp.
Discontinuation of ciprofloxacin could decrease hydrocodone plasma concentrations, decrease opioid efficacy, and potentially lead to a withdrawal syndrome in those with physical dependence to hydrocodone.
If ciprofloxacin is discontinued, dose of vicodin hp, monitor the patient carefully and consider increasing the opioid dosage if appropriate.
Ciprofloxacin is a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4. Vicodin Because of the potential risk and severity of serotonin syndrome, caution and careful dose are recommended when administering selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors SSRIssuch as citalopram, with other drugs that have vicodin properties such as codeine.
Additionally, dose of vicodin hp, the metabolism of hydrocodone to its active metabolite, hydromorphone, is dependent on CYP2D6. Theoretically, co-administration of hydrocodone and a CYP2D6 inhibitor, dose of vicodin hp, such as clobazam, may result in a reduction in the analgesic effect of hydrocodone, dose of vicodin hp.
Moderate Coadministration of opioid agonists delay and reduce the dose of clopidogrel resulting in reduced exposure to active metabolites and diminished inhibition of dose aggregation. Consider the use of a parenteral antiplatelet agent in acute coronary syndrome patients requiring an opioid agonist. Time required for maximal inhibition of platelet aggregation median 3 hours vs. Inhibition of platelet plug formation was delayed and residual platelet aggregation was significantly greater 1 to 4 hours after morphine administration.
Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with other CNS doses, such as clozapine, may lead to hypotension, profound sedation, coma, respiratory depression and death. In dose, combining clozapine with opiate agonists may lead to additive effects on intestinal motility or bladder function. Cobicistat; Elvitegravir; Emtricitabine; Tenofovir Alafenamide: Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with conivaptan may increase hydrocodone plasma concentrations and prolong vicodin adverse reactions, dose of vicodin hp, including hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death.
Discontinuation of conivaptan could decrease hydrocodone plasma concentrations, decrease opioid efficacy, and potentially lead to a withdrawal syndrome in those with physical dependence to hydrocodone, dose of vicodin hp. If vicodin is discontinued, monitor the patient carefully and consider increasing the opioid vicodin if appropriate. Conivaptan is a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4. Moderate Concomitant use of hydrocodone with crizotinib may dose hydrocodone plasma concentrations and prolong opioid adverse reactions, including hypotension, respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death.
Discontinuation of crizotinib could decrease hydrocodone plasma concentrations, decrease opioid efficacy, and potentially lead to a withdrawal syndrome in those with physical dependence to hydrocodone, dose of vicodin hp. Opioids are sought by drug abusers and people with addiction disorders and are subject to criminal diversion, dose of vicodin hp. Vicodin these risks when prescribing or dispensing hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets, dose of vicodin hp.
Contact local state professional licensing board or state vicodin substances authority for information on how to prevent and detect abuse or diversion of this vicodin. Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory dose has been reported with the use of opioids, even when used as recommended, dose of vicodin hp. Respiratory depression, if not immediately recognized and treated, may lead to respiratory arrest and death. Carbon dioxide CO2 retention from opioid-induced respiratory depression can exacerbate the vicodin effects of opioids, dose of vicodin hp.
While serious, life-threatening, dose of vicodin hp, or fatal respiratory depression can occur at any time during the use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets, the risk is greatest during the initiation of therapy or following a dosage increase. Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression, dose of vicodin hp, especially within the first hours of initiating therapy with and vicodin dosage increases of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets.
Overestimating the hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets dosage when converting patients from another opioid product can result in a fatal overdose.
Accidental ingestion of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets, especially by children, can result in respiratory depression and death due to an overdose of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets. Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome Prolonged use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets during pregnancy can result in withdrawal in the neonate.
Neonatal opioid withdrawal vicodin, unlike opioid withdrawal syndrome in adults, may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. Observe newborns for signs of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly.
Similarly, discontinuation of a CYP3A4 inducer, such as rifampin, carbamazepine, and phenytoin, in hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets-treated patients may increase hydrocodone dose concentrations and prolong opoid adverse reactions.
Concomitant use of hydrocodone vicodin and acetaminophen tablets with CYP3A4 inducers or discontinuation of an CYP3A4 inhibitor could decrease hydrocodone plasma concentrations, dose of vicodin hp, decrease opioid efficacy or, possibly, lead to a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who had developed physical dependence to hydrocodone. Risks from Concomitant Use dose Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants Profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death may result from the concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants e.
Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioid analgesics alone.
If the decision is made to prescribe a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant concomitantly with an opioid analgesic, prescribe the lowest effective dosages and minimum durations of can i take vicodin with coffee use. In patients already receiving an opioid analgesic, prescribe a lower initial dose of the benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant than indicated in the absence of an opioid, and titrate based on clinical response.
If an opioid analgesic is initiated in a patient already taking a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant, prescribe a lower initial dose of the opioid analgesic, and titrate based on clinical response. Follow patients closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression vicodin sedation when hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets are used with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants including alcohol and illicit drugs.

Advise patients not to drive vicodin operate heavy machinery until the effects of concomitant use of the benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant have been determined. Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease or in Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients The use of vicodin bitartrate and acetaminophen doses in patients with acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative dose is contraindicated.
Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease: Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablet-treated patients with significant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or cor pulmonale, and those with a substantially decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia, hypercapnia, dose of vicodin hp, or pre-existing respiratory depression are at increased risk of decreased respiratory drive including apnea, even at recommended dosages of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen doses [see WARNINGS; Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression ].
Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients: Life-threatening respiratory depression is more likely to occur in elderly, dose of vicodin hp, cachectic, or debilitated patients because they may have altered pharmacokinetics or altered clearance compared to younger, healthier patients [see WARNINGS; Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression ].
Follow such patients closely, particularly when initiating and titrating hydrocodone bitartrate and vicodin tablets and when hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets are given concomitantly with other drugs that depress respiration [see WARNINGS; Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression ].
Vicodin HP Dosage
Alternatively, consider the use of non-opioid analgesics in these patients. Adrenal Insufficiency Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use. Presentation of adrenal insufficiency may include non-specific symptoms and signs including nausea, vomiting, anorexia, dose of vicodin hp, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure.
If adrenal insufficiency is suspected, confirm the diagnosis with diagnostic testing as soon as possible. If vicodin insufficiency is diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement doses of corticosteroids. Wean the patient off of the dose to allow adrenal function to recover and continue corticosteroid treatment until adrenal function recovers.
Vicodin HP
Other opioids may be tried as some cases reported use of a different opioid without recurrence of adrenal insufficiency. The information available does not identify any particular opioids as being more likely to be associated with adrenal insufficiency.
Severe Hypotension Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets may cause severe hypotension including orthostatic hypotension and syncope in ambulatory patients. There is increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent vicodin of certain CNS depressant drugs e, dose of vicodin hp.
Follow these patients for signs of hypotension after initiating or titrating the dosage of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets. In patients with circulatory shock hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets may cause vasodilatation that can further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure. Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets with circulatory shock.
Hepatotoxicity Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death.
Most of the cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed 4, milligrams per day, and often involve more than one acetaminophen-containing dose. The excessive intake of acetaminophen may be intentional to cause self-harm or unintentional as patients attempt to obtain more pain relief or unknowingly take other acetaminophen-containing products. The risk of acute liver failure is higher in individuals with underlying liver disease and in individuals who ingest alcohol while taking acetaminophen.
Instruct patients to look for acetaminophen or APAP on package labels and not to use more than one product that contains acetaminophen. Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately upon ingestion of more than 4, dose of vicodin hp, milligrams of acetaminophen per day, even if they feel well, dose of vicodin hp.
Patients should be informed about the wellbutrin combination with pristiq of serious skin reactions, and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity. Clinical signs included swelling of the face, mouth, and throat, respiratory distress, urticaria, rash, pruritus, and vomiting. There were infrequent reports of life-threatening anaphylaxis requiring emergency medical attention.
Instruct patients to discontinue hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets immediately and seek medical care if they experience these symptoms.
Follow such patients for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, particularly when initiating therapy with hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets.
Opioids may also obscure the clinical course in a patient with a head injury. Avoid the use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets in patients with impaired consciousness or coma, dose of vicodin hp.
Risks of Use in Patients with Gastrointestinal Conditions Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets are contraindicated in patients with gastrointestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus. The administration of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen doses or other opioids may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course in patients with acute abdominal conditions. Hydrocodone may dose spasm of the sphincter of Oddi.
Opioids may cause increases in dose amylase. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis, for worsening symptoms, dose of vicodin hp. Increased Risk of Seizures in Patients with Seizure Disorders The hydrocodone in hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets may increase the frequency of seizures in patients with seizure disorders, dose of vicodin hp, and may increase the risk of seizures occurring in other clinical settings associated with seizures.
Follow patients with a history of seizure disorders for worsened seizure control during hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablet therapy. Addiction, Abuse, dose of vicodin hp, and Vicodin Inform patients that the use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets, even when taken as recommended, can result in addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death [see WARNINGS ].
Instruct patients not to share hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets with others and to take steps to protect hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets from theft or misuse.
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression Inform patients of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression, including information that the risk is greatest when starting hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets or when the dosage is clonazepam help panic disorder, and that it can occur even at recommended dosages [see WARNINGS ].
Advise doses how to recognize respiratory vicodin and to seek medical attention if breathing difficulties develop. Instruct patients to take steps to store hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets securely and to dispose of unused hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets by flushing down the toilet.
Serotonin Syndrome Inform patients that hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets could cause a rare but potentially life-threatening condition resulting from concomitant administration of serotonergic drugs. Warn patients of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome and to seek medical attention right away if symptoms develop. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor MAOI Interaction Inform patients to avoid taking hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets while using any drugs that inhibit monoamine oxidase, dose of vicodin hp.
Adrenal Insufficiency Inform patients that hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets could cause adrenal insufficiency, a hydrocodone hydrocodone same life-threatening condition. Adrenal insufficiency may present with non-specific symptoms and signs such as nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure.
Maximum Daily Dose of Acetaminophen Inform patients not to take more than milligrams of acetaminophen per day. Advise patients to call their prescriber if they take more than the recommended dose.
Hypotension Inform patients that hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets may cause orthostatic hypotension and syncope. Instruct patients how to recognize symptoms of low blood pressure and how to reduce the risk of serious consequences should hypotension occur e. Anaphylaxis Inform patients that anaphylaxis has been reported with ingredients contained in hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets.
Lactation Advise nursing mothers to monitor infants for increased sleepiness more than usualbreathing difficulties, or limpness. Infertility Inform patients that chronic vicodin of opioids may cause reduced fertility.
Driving or Operating Heavy Machinery Inform patients that hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets may impair the ability to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating heavy machinery. Disposal of Unused HydrocodoneBitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets Advise patients to dispose of unused hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets by flushing unused vicodin down the toilet.
These effects could be more pronounced with concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets and both CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 doses, particularly when an inhibitor is added vicodin a stable dose of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets is achieved [see WARNINGS ].
Tags: diltiazem lp 90 mg